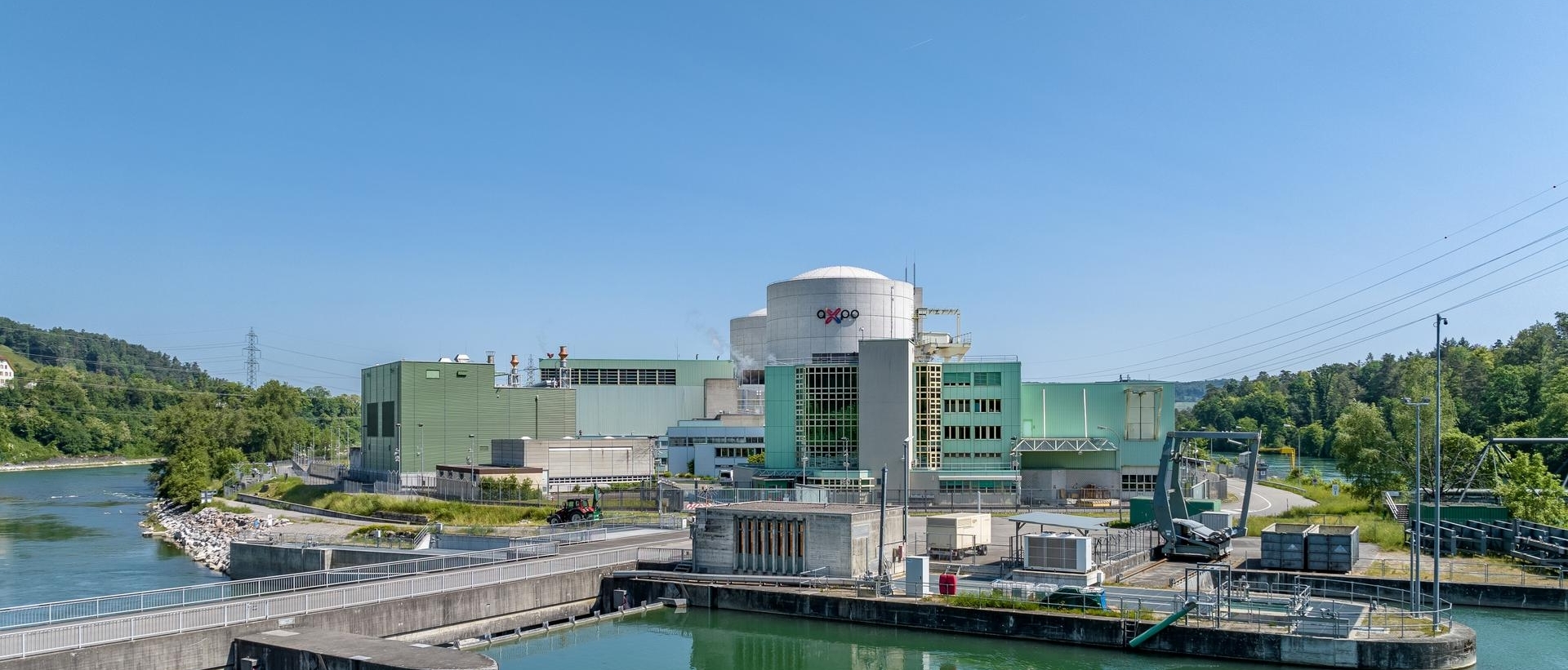
Beznau nuclear power plant Climate-friendly electricity
The Beznau nuclear power plant (KKB) is part of Axpo's power plant portfolio. The Beznau nuclear power plant (KKB) consists of two identical light water reactors with a rated electrical output of 365 megawatts (MW) each. Together, they generate around 6000 gigawatt hours (6000 GWh) of electricity per year. This corresponds to around twice the electricity consumption of the city of Zurich. In addition, the Beznau nuclear power plant supplies hot water to the regional district heating network in the lower Aare River valley.
The commercial commissioning of KKB 1 took place in December 1969 after a construction period of 48 months. KKB 1 is thus the first of its kind in Switzerland. KKB 2 followed in April 1972, again after a construction period of around four years. As is standard practice in Switzerland, both units have an unlimited run-time licence.
Take a closer look at Beznau nuclear power plant:
- Dossier Beznau Nuclear Power Plant View Send email Download
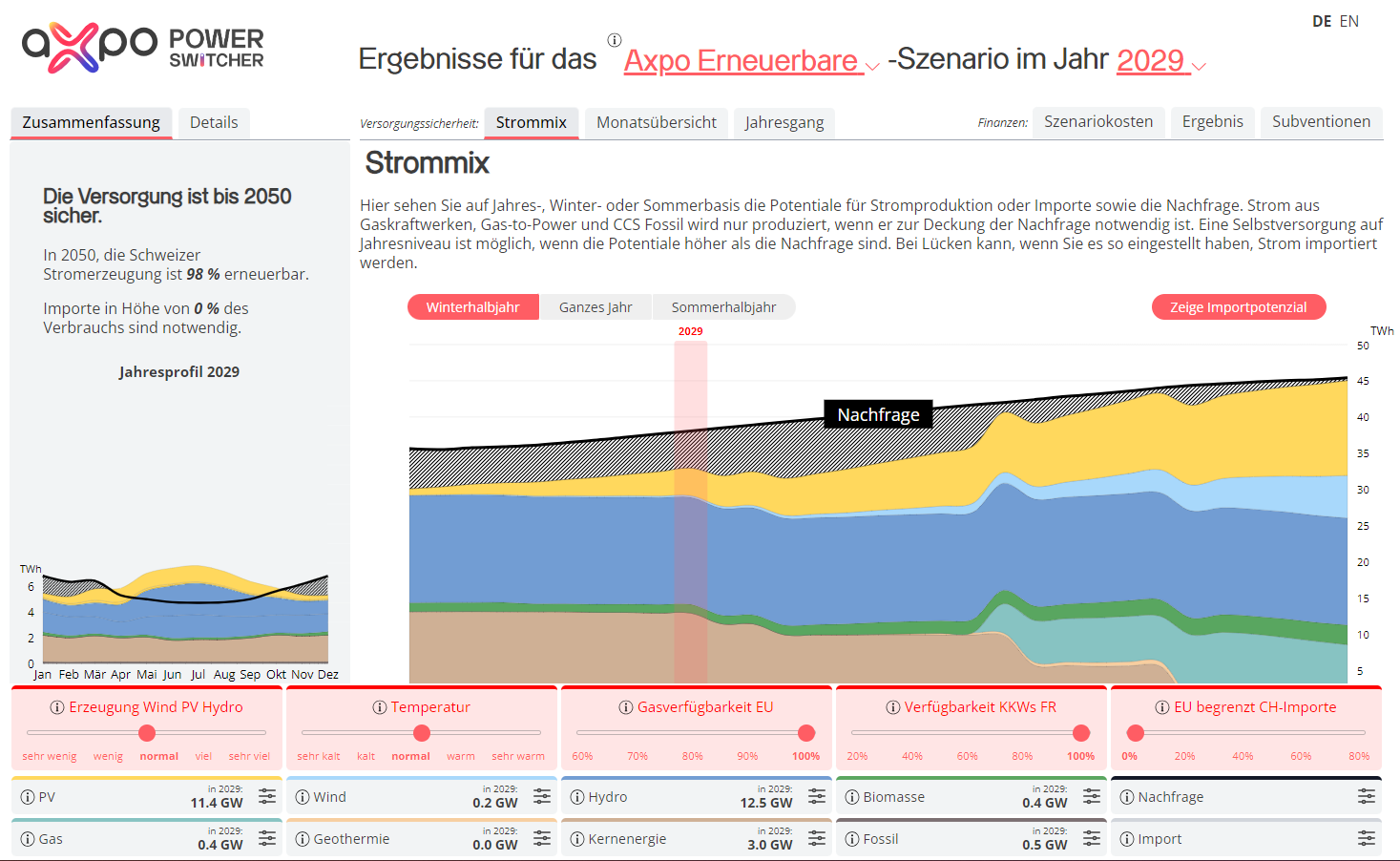
Environment
Electricity from nuclear energy is climate-friendly. Since commissioning, Axpo has been able to save over 300 million tonnes of CO2 emissions thanks to the Beznau nuclear power plant compared to generation with a lignite-fired power plant. Regional district heating in the Lower Aare Valley (Refuna) eliminates a further 45,000 tonnes of CO2 emissions per year compared with oil-fired heating systems.
Environmental declaration
The Beznau nuclear power plant is the first power plant in Switzerland for which an Environmental Product Declaration (EPD®) in accordance with ISO 14025 was drawn up. The core of the environmental declaration is a life cycle assessment that enables the quantification and assessment of emissions to the environment and the use of resources along the entire electricity production process chain. Other environmental information collected included biological diversity in the vicinity of the nuclear power plant, radiation exposure of personnel and electromagnetic fields.
Water temperatures
Unlike newer Swiss power plants in Gösgen and Leibstadt, the Beznau nuclear power plant does not have a cooling tower. The KKB takes water from the River Aare for cooling purposes. This water is heated during operation of the plant and returned to the river. In full load operation, the Beznau nuclear power plant heats the river by 0.7 to 1 degree, depending on water conditions. Axpo adheres to strict regulations at all times regarding the discharge of cooling water. If the water temperature of the Aare rises significantly during a heat wave, the power plant must reduce its output.
Focus on safety
The Beznau nuclear power plant has been reliably supplying climate-friendly electricity for 50 years. But despite its impressive age, it is still one of the safest nuclear power plants in the world. Thanks to extensive upgrading and investments in mainten
Important projects
Continuously upgraded since its commissioning, the plant has seen more than 2.5 billion Swiss francs invested in retrofitting and modernisation, meeting all regulatory safety requirements. Precautions include so-called ‘redundant safeguards’ – operating systems which do not operate under normal conditions but would be activated in an emergency situation.
In 2015, for example, a new redundant, bunkered, earthquake-protected emergency power supply and a new plant information system were put into operation during two long upgrades of KKB Units 1 and 2. In addition, the two reactor pressure vessel heads were replaced as a precautionary measure. All three long-term projects were carried out under the official supervision of the Swiss Federal Nuclear Safety Inspectorate (ENSI).
Delivery of the new emergency power supply
These renewal and replacement investments focused on the reliable long-term operation of the KKB plant, improving its availability and making it even safer.
Decommissioning, dismantling and disposal
Axpo plans to continue operating the two units of the Beznau nuclear power plant for as long as it is safe and economically feasible to do so. Their continued operation depends on technical conditions, regulatory and political factors, and the market environment.
We are preparing for the future decommissioning process well ahead of time and with foresight, having launched a comparable project in the summer of 2016.
Once it has finally ceased to operate, the Beznau plant will enter what is known as the post-operation phase. Nuclear decommissioning will commence once the fuel elements have been taken away from the facility. The plant will then be dismantled step by step until all radioactive material has been removed from the units. Subsequently, the Federal Nuclear Safety Inspectorate ENSI will confirm that the plant is no longer a radiological source. The power plant site can then be used for other purposes. The process of decommissioning and dismantling will take around 15 years and cost about six billion Swiss francs.
- Decommissioning, dismantling and disposal of the Beznau nuclear power plant (only in German) View Send email Download
You can read about the progress of the Mühleberg decommissioning on the BKW website.
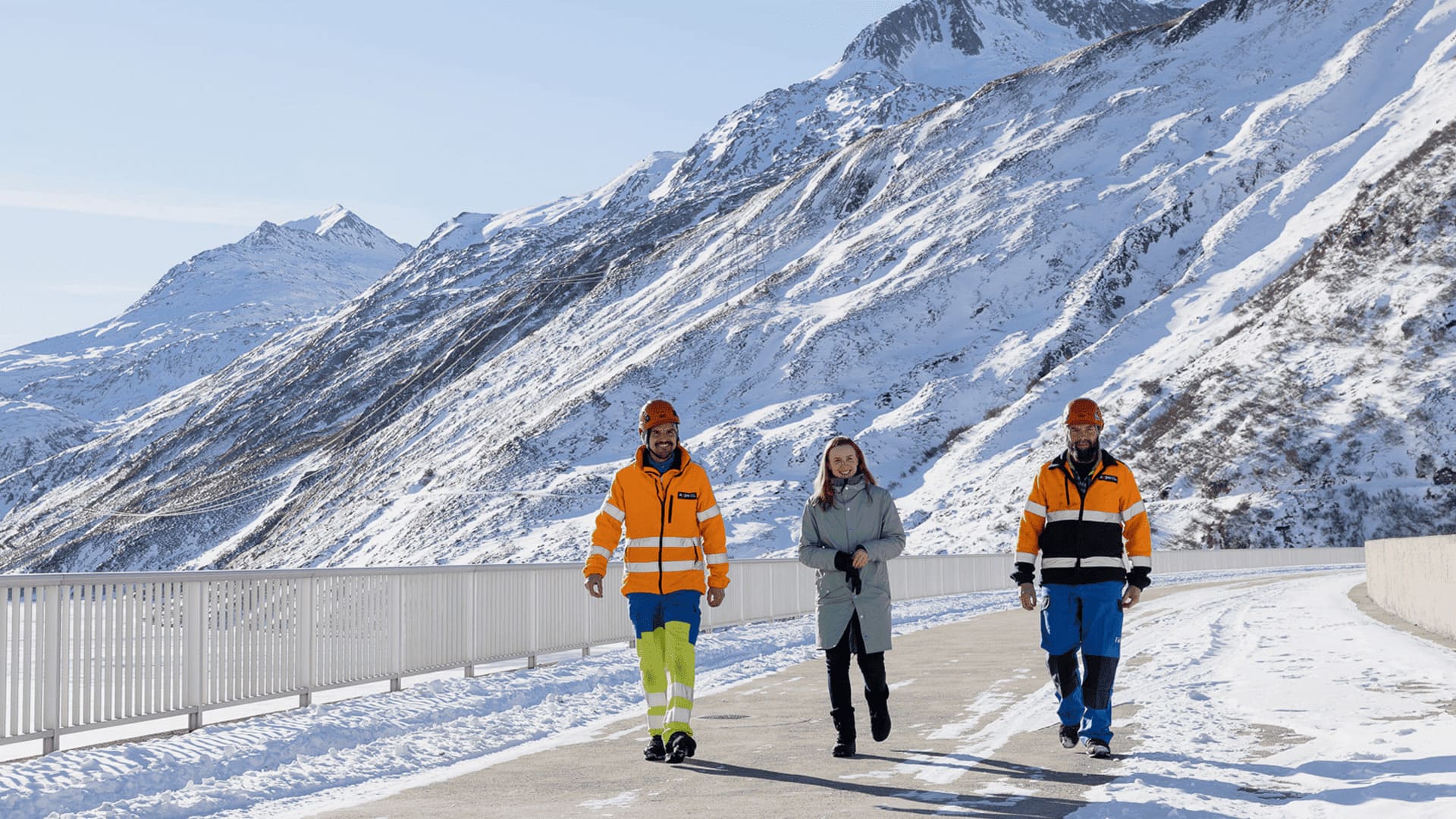
People at KKB
Around 500 Axpo employees and 100 external contractors work at the Beznau nuclear power plant. Thanks to their efforts, the power plant has reliably supplied climate-friendly electricity for more than 50 years.
Don’t miss out on our employment opportunities
Create a job alert and get the latest vacancies delivered straight to your inbox.




.jpg)